Nepal yet to make good on its promise to WTO
Quick look
Particulars
Total
Completed
Pending
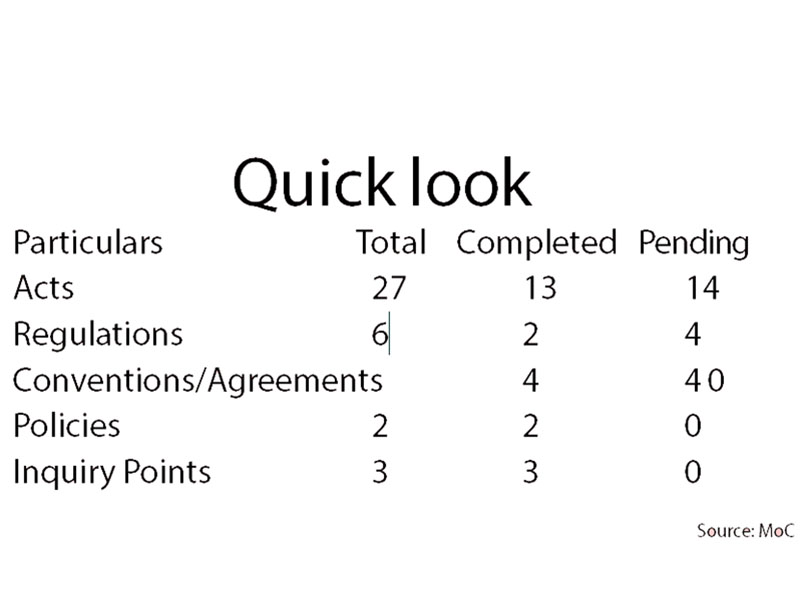
Acts
27
13
14
Regulations
6
2
4
Conventions /Agreements
4
40
Policies
2
2
Inquiry Points
3
3
Kathmandu, Sept 13
Over 12 years since Nepal’s accession to the World Trade Organisation, the country is yet to amend and formulate 14 acts and four regulations that were committed while obtaining membership of the multilateral trading system.
The country had made a commitment to amend prevailing laws and regulations to make them compatible with the provisions of the multilateral trading regime. The country had also pledged to formulate some of the laws and regulations at the earliest, but the 18 laws and regulations out of the total 33 pledged are yet to be harmonised and formulated, according to Mina Aryal, undersecretary at the Ministry of Commerce (MoC).
The laws that are yet to be either amended or formulated include Export-Import (Control) Act 1957; Law on Anti-dumping Measures; Nepal Standards (Certification Mark) Act, 1980; Environment Act, 1997; Industrial Property (Protection) Act; Plant Resources Act; Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act, 1992; Access to Genetic Resources Act; Labour Act, 1991; Nepal Bar Council Act, 1992; Health Institutions Operating Act; Insurance Act, 1992 and Pharmaceutical Act, according to the MoC.
Some of the laws like Law on Anti-dumping Measures are yet to be introduced. The law would authorise the country to slap tariff and other measures against certain products of foreign countries that dump their products in Nepal at below production cost.
When cheaper goods enter the market, it can harm the production and manufacturing base of the country. However, the country has not formulated such an act to safeguard the country’s production and manufacturing base.
Similarly, some of the policies and regulations related with aforementioned laws need to be amended, like, Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Regulations, Nepal Standards (Certification Mark) Regulations and Export-Import (Control) Regulations, among others.
Likewise, the country has yet to ratify international convention — Instruments of Ratification for United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (Vienna, 1980).