Get rid of urinary tract infection
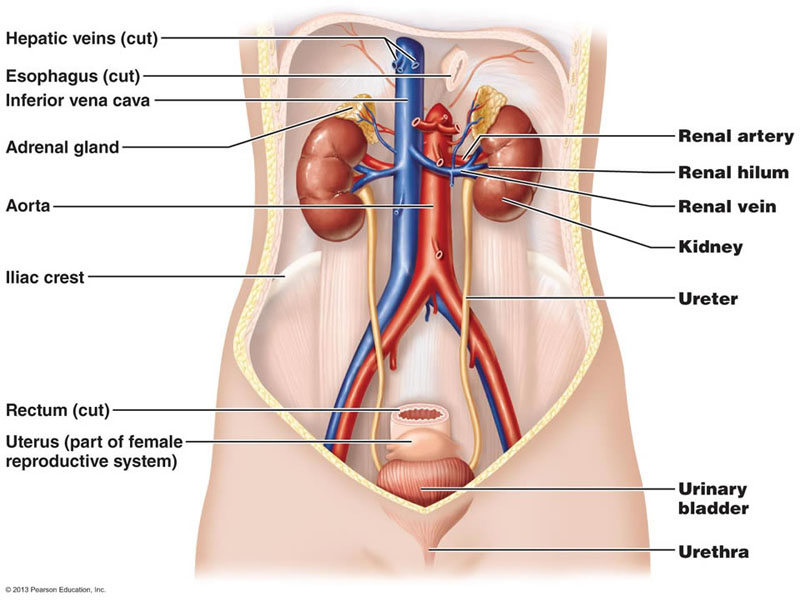
Urine is formed in the kidneys. From kidneys, the urine passes through the ureters to the bladder where it is stored. During urination this urine passes out of the body through urethra. Kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra are the parts of human’s urinary system. One may suffer from various problems in the urinary system, and Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is one of the common problems.
UTI is the infection in any part of urinary system. “The upper urinary tract is composed of the kidneys and ureters. And infection in these organs is upper urinary tract infection. An infection in the lower urinary tract — bladder and urethra — is called lower urinary tract infection,” Dr Bharat Bhandari, Uro Surgeon at Norvic International Hospital, Thapathali and Sumeru Hospital, Dhapakhel explains.
There are various causes of UTI and they are different as per the age groups. “For children congenital anomalies, holding urine (either as a habit or due to burning sensation when urinating) and defect in anatomy are some causes of UTI. Especially female children, who do not wear underwear, can get a UTI,” Dr Bhandari shares about the causes adding, “In young women, UTI can occur after sexual intercourse — especially in the initial months, as women may suffer from sexual trauma.”
Men also can get UTI when “they suffer from prostate disease. It usually happens after the age of 40-50 when the bladder doesn’t empty urine properly. As a result, bacteria colonise in the bladder leading to UTI”.
Some other causes of UTI are stent, fungal infection, and tuberculosis in the urinary system. Viral infection can also lead to the UTI.
Symptoms
Whenever one suffers from the UTI, one feels a strong urge to urinate. Burning sensation while urinating, passage of frequent and small amount of urine, fever, chills, sweating, pain in joints are other symptoms of UTI as per the doctor. Heaviness and pain in the lower abdomen are also common.
Of chronic symptoms, he adds, “If the infection is chronic then there is whitish discharge in urine, discharge of blood in urine and urine smells strong. However, people might not suffer from fever if they have chronic infection.”
Common in women
Both male and female can get UTI, but it is common in women because of their anatomy.
“In females, urethra (that transports urine out of human body) is near to the anus. So, Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria, usually found in the intestine, can enter the bladder through urethra, causing the infection. The infection can then move up to the kidneys also. The blood can at times transport bacteria to the kidneys, causing the UTI,” he elaborates.
Menopausal infection is yet another cause of the UTI in women as per the doctor. After menopause there is hormonal changes in women, and it weakens their defence mechanism. This hormonal change also weakens the defence system of urinary bladder and urethra. The bacteria then attacks the urinary system and women suffer from UTI.
And so “the risk of the UTI is high as women get older”.
Besides, those with compromised immune system, those on medication, and those who haven’t completed their dose of medication, are also under the risk of getting the infection, he informs.
Take care
“Bacteria has the tendency to hang on in the urinary tract using hooks, and one needs to break that hook and flush out the bacteria to get rid of the infection. For that, women (if not diabetic), can drink a glass of cranberry juice daily. The juice helps in breaking the hooks, and then flushes out the bacteria, and prevents the (re)occurrence of UTI,” the doctor reveals.
Hygiene is another important factor to keep UTI at bay. Dr Bhandari points out, “If women do not maintain personal hygiene, they may suffer from the infection. Trauma during the sexual intercourse, wet and exposed private organs are some other causes for the bacteria to germinate.” So, he advises to maintain personal hygiene like changing underwear timely.
When UTI is diagnosed, the disease should be treated. If left untreated, complications like “scar in the kidney(s), irreversible kidney damages, heart problems due to toxins of bacteria and sepsis” can be seen. “Frequent recurrence of UTI can also scar the kidney(s) and damage it. Side effects of medicines given for the UTI too can affect kidney(s),” Dr Bhandari reveals.
- Test your urine once in six months or once in a year
- Maintain personal hygiene
- Treat your diseases
- Use clean toilets (Avoid contact and contamination)
- Take medicinesas prescribed by the doctors
- Drink water frequently to flush 1.5 to two litres of urine per day